Interview about our article at Focus Magazine
Liver metastasis directed radiotherapy with UNITY 1.5 Tesla MR-linac

Merdan FAYDA, MD, Professor of Radiation Oncology
Between 1993-1999, I completed my undergraduate education at Istanbul University Faculty of Medicine. Between 1999-2004, I worked at Istanbul University, Istanbul Faculty of Medicine, as a Radiation Ongology Resident... Continued...Radiation Oncology
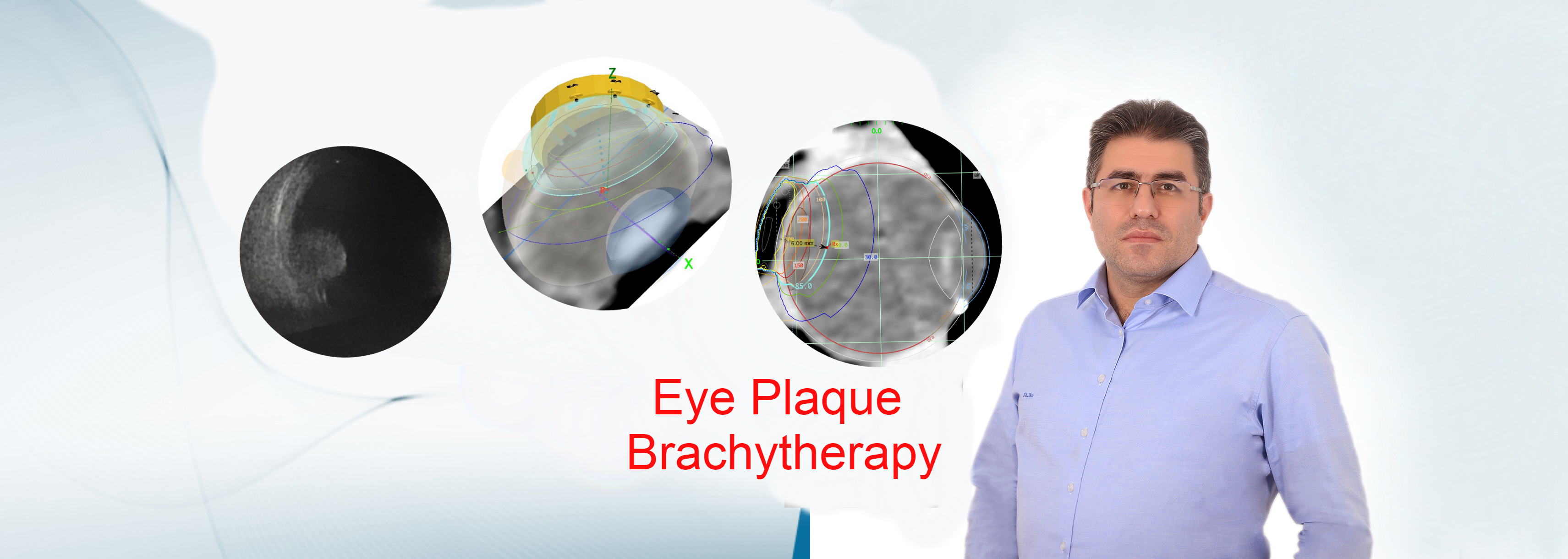
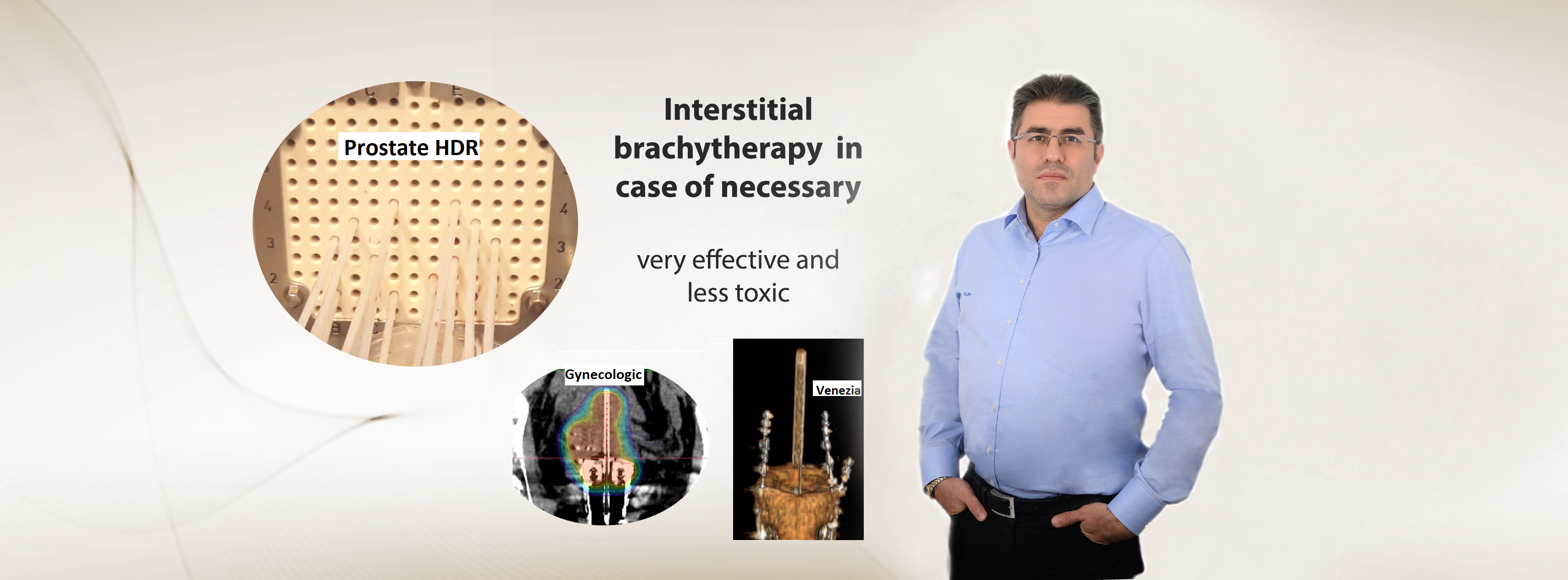
Today, the main methods effective in the treatment of cancer; surgery, systemic treatments (chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapies, immunotherapy) and radiation therapy. Radiation therapy was introduced immediately after Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered the X-ray in 1895. Over the years, both radiation generation and application have become increasingly modern and more reliable. Advances in magnetic resonance, computed tomography, and PET-CT technology help to select better patients for radiotherapy and to provide more accurate radiotherapy. Image-based radiotherapy based on three-dimensional cross-sectional anatomy enables more effective and less side-effect radiotherapy.
More than 30% (*) of cancer deaths can be prevented by changing or avoiding key risk factors:
• Tobacco use• Being overweight / obese
• Unhealthy diets with low consumption of fruits and vegetables
• Lack of physical activity
• Alcohol use
• Sexually transmitted HPV infection
• Hepatitis-B infection
• Ionizing (occupational, medical imaging) and non-ionizing radiation (sunlight, solarium)
• Urban air pollution
• Inhalation of solid fuel gases in the house
*WHO cancer Fact Sheet No: 297
10 facts about radiotherapy according to the European Society of Radiation Oncology (ESTRO)
•At least one-fourth of cancer patients are unable to receive radiotherapy despite their need.• In 2025, the need for radiotherapy will increase by 16% compared to today, and today's infrastructure is not sufficient to meet this need
• By 2035, 1 million lives can be saved all over the world if radiotherapy can be applied to anyone in need.
• Radiotherapy saves lives and is the main treatment for many types of cancer.
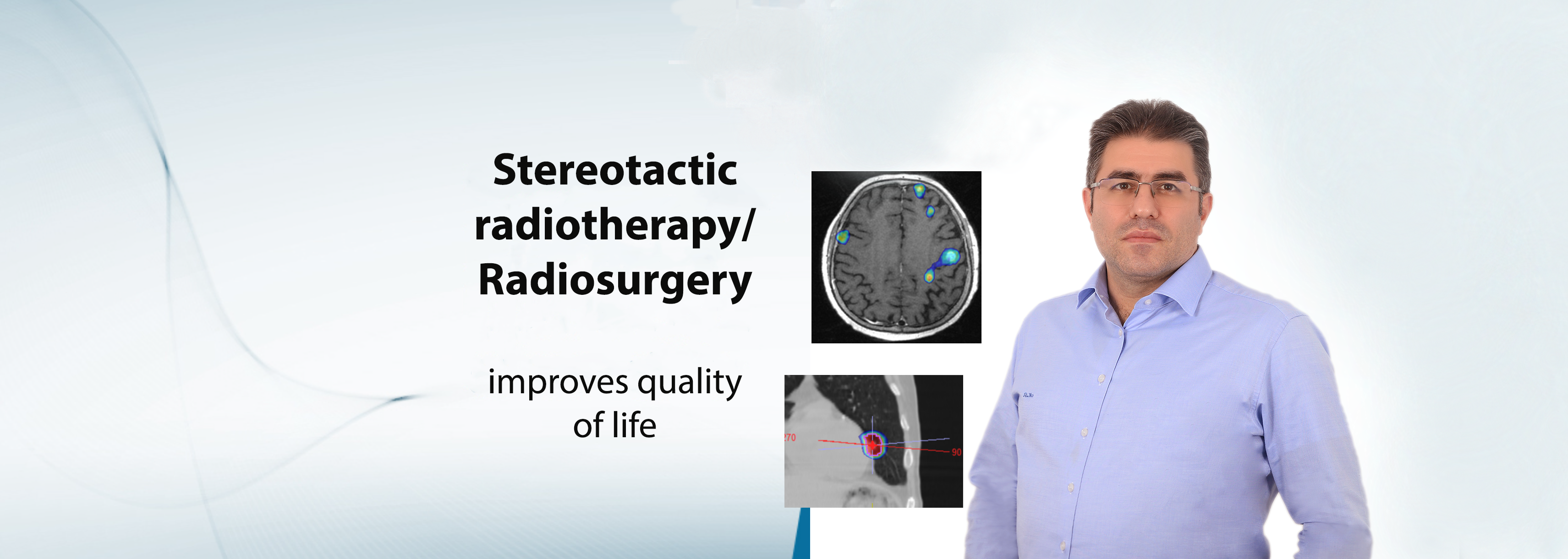
• Radiotherapy relieves cancer complaints such as pain and improves the quality of life of patients.
• Since radiotherapy is not usually an invasive procedure, most patients who enter radiotherapy can work and continue their daily lives.
• State of art radiotherapy irradiates the tumor evenly, thereby causing less damage to healthy organs and tissues near the irradiated area.
• Ongoing improvements in radiotherapy have begun to shorten the duration of treatment. For example, the duration of treatment in breast and prostate cancers has been halved in the last 20 years.
• Advances in radiotherapy have led to more patients receiving treatment, as is the case for non-surgical patients.
• There is a significant difference across Europe in terms of radiotherapy treatment, services and access to trained staff.
***Source***